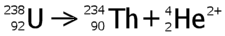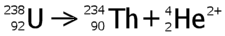| Alpha decay is one process that unstable atoms can use to become more stable. During alpha decay, an atom's nucleus sheds two
protons
and two
neutrons
in a packet that scientists call an alpha particle. |
| Since an atom loses two
protons
during alpha decay, it changes from one element to another. For example, after undergoing alpha decay, an atom of
uranium
(with 92 protons) becomes an atom of
thorium
(with 90
protons
). |
| Alpha decay is a form of radioactive decay in which an atomic
nucleus
ejects an alpha particle through the electromagnetic force and transforms into a
nucleus
with mass number 4 less and atomic number 2 less. For example: |
|
|
| this is usually written as; |
|
|
| Note that an alpha particle IS a
helium
nucleus, and that both mass number and
atomic number
are conserved. Alpha decay can essentially be thought of as nuclear fission where the parent
nucleus
splits into two daughter
nuclei
. Alpha decay is fundamentally a quantum tunneling process. Unlike beta decay, alpha decay is governed by the strong nuclear force. |
| Alpha particles with their typical kinetic energy of 5
MeV
have a speed of 15,000 km/s. |
| Because of alpha decay, virtually all of the
helium
produced in the United States and elsewhere comes from trapped underground deposits associated with minerals containing
uranium
or
thorium
, and brought to the surface as a by-product of natural gas production. |
| Alpha particles emitted by radioactive
nuclei
are among the most hazardous forms of
radiation
, if these
nuclei
are incorporated within a human body. As any heavy charged particle, alpha particles lose their energy within a very short distance in dense media, causing significant damage to surrounding biomolecules. On the other hand, external alpha irradiation is not harmful because alpha particles are completely absorbed by a very thin (micrometers) dead layer of skin as well as by few centimeters of air. However, if a substance radiating alpha particles is injected, ingested or inhaled by an organism it may become a risk, potentially inflicting very serious damage to the organisms' genetic makeup. |